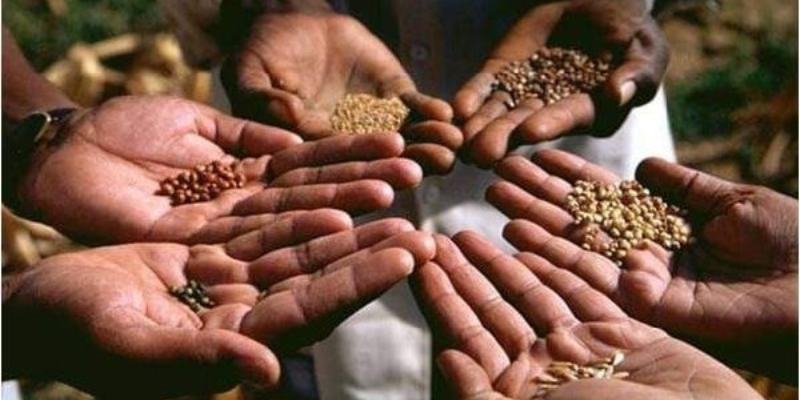

Agricultural
spacing for the chosen seeds.
₹10 raised of ₹25,000 goal 0.04%- 1 Donation
- Finalized
- 0 Likes
Campaign Ended!
Farming seeds are essential elements in agriculture, serving as the starting point for growing crops. These seeds can vary widely, encompassing a diverse range of plant species, each with its unique characteristics and requirements. Here is a general description of farming seeds:
- Variety and Types:
- Farming seeds come in various types, including vegetable seeds, grain seeds, fruit seeds, and more. Each type serves a specific purpose in agriculture, contributing to the production of a wide array of food crops.
- Genetic Diversity:
- Seeds carry the genetic information necessary for the development of plants. Maintaining genetic diversity is crucial for crop resilience, adaptability, and resistance to pests and diseases.
- Germination:
- Seeds undergo a process called germination, where they sprout and develop into seedlings. This marks the beginning of the plant's life cycle.
- Seed Coat:
- The outer layer of a seed, known as the seed coat, provides protection to the embryo inside. It may have various characteristics, such as hardness or softness, depending on the plant species.
- Storage Organs:
- Some seeds store nutrients within themselves to support the initial stages of plant growth. These storage organs, often part of the seed, provide energy for the developing seedling until it can generate its own through photosynthesis.
- Planting and Growth Conditions:
- Different seeds have specific requirements for planting and growth. Factors like soil type, temperature, moisture, and sunlight play a crucial role in the successful cultivation of seeds.
- Hybrid vs. Heirloom Seeds:
- Farmers can choose between hybrid and heirloom seeds. Hybrid seeds result from the crossbreeding of different varieties to achieve specific traits, while heirloom seeds are open-pollinated and often passed down through generations, maintaining traditional characteristics.
- Seed Quality and Viability:
- Seed quality is essential for successful farming. Farmers often test seed viability to ensure that a high percentage of seeds will germinate under favorable conditions.
- Seed Banks:
- To preserve genetic diversity and protect against the loss of valuable plant species, seed banks exist to store and safeguard seeds for future generations.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- With a growing focus on sustainable agriculture, there is an increasing interest in organic and non-GMO (Genetically Modified Organism) seeds. These seeds are cultivated without synthetic chemicals, promoting environmentally friendly and ethical farming practices.
-
Mahendran M donated ₹10